Inventor of the Camera Phone
 Philippe Kahn (b. 1952) was born in Paris, France to Jewish immigrants from Eastern Europe. His mother fought alongside the French in World War II (with the rank of lieutenant), and went on to survive Auschwitz. Kahn studied in Zurich and Nice, attaining master’s degrees in both mathematics and music. During his studies, he wrote software for the world’s first modern personal computer, the French-made MICRAL of 1973. In 1982, he started his own company in California called Borland. It was one of the first start-ups to create software development tools, and stood out from other companies as it offered incredibly cheap products. (Its Turbo Pascal, for example, cost only $50 compared to the thousands of dollars that similar tools cost.) Over the next ten years, Kahn transformed Borland into a computer powerhouse with $500 million in revenue. However, a number of disagreements led to the board squeezing him out of his own company. Kahn took his severance pay and started a new company, Starfish. Just a few years later, he sold it to Motorola for a whopping $325 million. Around this time, Kahn’s daughter was born, and he got frustrated at his inability to quickly send baby photos to friends and family. He fiddled with his camera and his phone until he managed to link the two. He then sent history’s first photograph through a cellphone. This inspired him to develop the camera-phone, making it the focus of his new startup, LightSurf Technologies. This company, too, was bought out for $300 million. Since then, Kahn has started yet another company that designs and develops wearable technology. He is also an avid sailor, holding the world record for fastest San Francisco to Hawaii trip, and recently winning the Transpacific Yacht Race from LA to Hawaii. Kahn is credited with inventing the now-ubiquitous camera phone, and TIME Magazine included his first phone photograph in its 2016 list of the 100 Most Influential Photos of All Time.
Philippe Kahn (b. 1952) was born in Paris, France to Jewish immigrants from Eastern Europe. His mother fought alongside the French in World War II (with the rank of lieutenant), and went on to survive Auschwitz. Kahn studied in Zurich and Nice, attaining master’s degrees in both mathematics and music. During his studies, he wrote software for the world’s first modern personal computer, the French-made MICRAL of 1973. In 1982, he started his own company in California called Borland. It was one of the first start-ups to create software development tools, and stood out from other companies as it offered incredibly cheap products. (Its Turbo Pascal, for example, cost only $50 compared to the thousands of dollars that similar tools cost.) Over the next ten years, Kahn transformed Borland into a computer powerhouse with $500 million in revenue. However, a number of disagreements led to the board squeezing him out of his own company. Kahn took his severance pay and started a new company, Starfish. Just a few years later, he sold it to Motorola for a whopping $325 million. Around this time, Kahn’s daughter was born, and he got frustrated at his inability to quickly send baby photos to friends and family. He fiddled with his camera and his phone until he managed to link the two. He then sent history’s first photograph through a cellphone. This inspired him to develop the camera-phone, making it the focus of his new startup, LightSurf Technologies. This company, too, was bought out for $300 million. Since then, Kahn has started yet another company that designs and develops wearable technology. He is also an avid sailor, holding the world record for fastest San Francisco to Hawaii trip, and recently winning the Transpacific Yacht Race from LA to Hawaii. Kahn is credited with inventing the now-ubiquitous camera phone, and TIME Magazine included his first phone photograph in its 2016 list of the 100 Most Influential Photos of All Time.
Words of the Week
The day science begins to study non-physical phenomena, it will make more progress in one decade than in all the previous centuries of its existence.
– Nikola Tesla
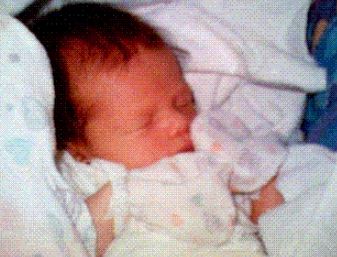
First photo taken and sent by a cellphone – June 11, 1997. TIME Magazine ranked it among the 100 Most Influential Photos of All Time.

 Chaim Gedaliah Rickover (1900-1986) was born in Poland. When he was six years old his family fled to the United States to escape the Russian pogroms that had killed over 3000 Jews in Eastern Europe. The family settled in Chicago, where Rickover started working at just nine years of age for three cents an hour. He excelled academically, and after graduating from high school with honours, was nominated by a Jewish congressman to the US Naval Academy. Rickover distinguished himself while serving on a destroyer ship and was among the youngest people to ever be promoted to an officer. He went back to school and earned a Master’s in electrical engineering before doing further studies at Columbia. At 29, he decided to serve on a submarine, and was soon in command of one. His translation of the German Das Unterseeboot became the textbook of the US Submarine Service. Throughout World War II, Rickover repaired electrical systems on US Navy ships, for which he earned the Legion of Merit. Following the war, he applied to join the Manhattan Project’s new program to develop nuclear power plants. He was soon the deputy manager of the division developing nuclear-powered navy ships. Rickover saw that the greatest potential was for nuclear submarines, and ultimately succeeded in persuading the Secretary of the Navy to endorse building one. Rickover led its development, and played a central role in designing a nuclear reactor fit for submarines. His vision came to life in 1954 with the launch of the famous USS Nautilus. It put him on the cover of TIME Magazine that year. By 1958, Rickover was vice admiral of the Navy, and awarded a Congressional Gold Medal. His program would go on to produce over 200 nuclear-powered submarines, and 23 aircraft carriers and cruisers. Incredibly, none of these has ever had a meltdown – a feat credited to Rickover’s insistence on safety and obsessive attention to detail. (The Soviet Navy suffered at least 14 meltdowns in the same time period!) Rickover became known as the “Father of the Nuclear Navy”. He was the longest serving officer in US naval history, with 63 years of service under 13 presidents. A four-star admiral, his 61 civilian awards included a Presidential Medal of Freedom and two Congressional Gold Medals (an extremely rare feat). He was also awarded 15 honourary degrees, and made an honourary Commander of the Order of the British Empire. Rickover stated that he was not proud of his work, and saw it as a “necessary evil” to protect his country. He once said he wished “nuclear power had never been discovered” and hoped that the nuclear fleet would be dismantled.
Chaim Gedaliah Rickover (1900-1986) was born in Poland. When he was six years old his family fled to the United States to escape the Russian pogroms that had killed over 3000 Jews in Eastern Europe. The family settled in Chicago, where Rickover started working at just nine years of age for three cents an hour. He excelled academically, and after graduating from high school with honours, was nominated by a Jewish congressman to the US Naval Academy. Rickover distinguished himself while serving on a destroyer ship and was among the youngest people to ever be promoted to an officer. He went back to school and earned a Master’s in electrical engineering before doing further studies at Columbia. At 29, he decided to serve on a submarine, and was soon in command of one. His translation of the German Das Unterseeboot became the textbook of the US Submarine Service. Throughout World War II, Rickover repaired electrical systems on US Navy ships, for which he earned the Legion of Merit. Following the war, he applied to join the Manhattan Project’s new program to develop nuclear power plants. He was soon the deputy manager of the division developing nuclear-powered navy ships. Rickover saw that the greatest potential was for nuclear submarines, and ultimately succeeded in persuading the Secretary of the Navy to endorse building one. Rickover led its development, and played a central role in designing a nuclear reactor fit for submarines. His vision came to life in 1954 with the launch of the famous USS Nautilus. It put him on the cover of TIME Magazine that year. By 1958, Rickover was vice admiral of the Navy, and awarded a Congressional Gold Medal. His program would go on to produce over 200 nuclear-powered submarines, and 23 aircraft carriers and cruisers. Incredibly, none of these has ever had a meltdown – a feat credited to Rickover’s insistence on safety and obsessive attention to detail. (The Soviet Navy suffered at least 14 meltdowns in the same time period!) Rickover became known as the “Father of the Nuclear Navy”. He was the longest serving officer in US naval history, with 63 years of service under 13 presidents. A four-star admiral, his 61 civilian awards included a Presidential Medal of Freedom and two Congressional Gold Medals (an extremely rare feat). He was also awarded 15 honourary degrees, and made an honourary Commander of the Order of the British Empire. Rickover stated that he was not proud of his work, and saw it as a “necessary evil” to protect his country. He once said he wished “nuclear power had never been discovered” and hoped that the nuclear fleet would be dismantled.