The War Hero Archaeologist Who Made a Revolutionary Discovery
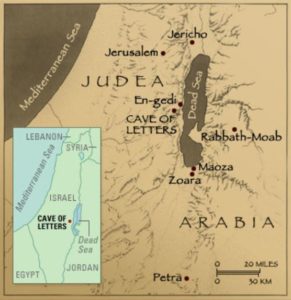
Babatha bat Shimon (c. 104-132 CE) was born in the town of Mahoza by the Dead Sea to a wealthy Jewish family originally from Ein Gedi. It was in this area that Israeli archaeologist Yigael Yadin discovered a leather pouch with her belongings in 1960. The documents inside included her legal, financial, and marriage contracts, presenting an eye-opening picture of the life of an upper-class Jewish woman two millennia ago. An only child, Babatha inherited all of her father’s date palm orchards when he passed away. She married her first husband, a man named Yeshu, while still a teenager. He died several years later, after which she married another date farmer named Yehuda. One of the discovered documents shows that Babatha lent her husband a sizeable loan (interest-free, of course). When he also passed away, Babatha seized all of his property as collateral. The documents reveal a number of legal battles that Babatha had to overcome, as well as her impressive financial and business acumen. She spoke several languages and was well-educated. During the Bar Kochva Revolt, Babatha fled from the Romans and hid in a cave, together with one of Bar Kochva’s generals, named Yonatan. It is believed she was killed in the war shortly after. Archaeologist Richard Freund has said that Babatha “revolutionized the way that we think about Jewish women in antiquity.”
 Yigael Sukenik (1917-1984) was born in Israel to Polish-Jewish parents. He joined the Haganah at 15, leaving several years later after a dispute with Yitzhak Sadeh. He decided to follow in his father’s footsteps and become an archaeologist. While studying at the Hebrew University he changed his last name to “Yadin”. When Israel’s Independence War broke out, Yadin returned to the newly-formed IDF and became the head of its operations. The following year, he became Chief of Staff. One of his first duties was going to Switzerland to study their army-reserve organization. He then created a similar reverse system in Israel. After resigning from the IDF to protest defence budget cuts, Yadin returned to academia. His doctoral thesis on a translation of the Dead Sea Scrolls won an Israel Prize. He travelled around the world to find and purchase lost and stolen Dead Sea Scrolls to return them to Israel. Meanwhile, Yadin excavated some of the most important archaeological sites in Israel, including Masada, Hazor, and Ein Gedi. During the Six-Day War, he returned to the military to advise the prime minister, and years later was part of the Agranat Commission that investigated the failure of the Yom Kippur War. As a result of this, he formed a new political party, Dash, which sought to fight corruption and restore confidence in Israel’s government. The party won a whopping 15 seats in its first election, and soon joined the new Likud coalition under Menachem Begin. Yadin became deputy prime minister, and played a critical role in the Camp David Accords. He wrote a number of bestselling books, taught at the Hebrew University for over 30 years, and was a renowned expert on the Qumran Caves, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and the Bar Kochva Revolt.
Yigael Sukenik (1917-1984) was born in Israel to Polish-Jewish parents. He joined the Haganah at 15, leaving several years later after a dispute with Yitzhak Sadeh. He decided to follow in his father’s footsteps and become an archaeologist. While studying at the Hebrew University he changed his last name to “Yadin”. When Israel’s Independence War broke out, Yadin returned to the newly-formed IDF and became the head of its operations. The following year, he became Chief of Staff. One of his first duties was going to Switzerland to study their army-reserve organization. He then created a similar reverse system in Israel. After resigning from the IDF to protest defence budget cuts, Yadin returned to academia. His doctoral thesis on a translation of the Dead Sea Scrolls won an Israel Prize. He travelled around the world to find and purchase lost and stolen Dead Sea Scrolls to return them to Israel. Meanwhile, Yadin excavated some of the most important archaeological sites in Israel, including Masada, Hazor, and Ein Gedi. During the Six-Day War, he returned to the military to advise the prime minister, and years later was part of the Agranat Commission that investigated the failure of the Yom Kippur War. As a result of this, he formed a new political party, Dash, which sought to fight corruption and restore confidence in Israel’s government. The party won a whopping 15 seats in its first election, and soon joined the new Likud coalition under Menachem Begin. Yadin became deputy prime minister, and played a critical role in the Camp David Accords. He wrote a number of bestselling books, taught at the Hebrew University for over 30 years, and was a renowned expert on the Qumran Caves, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and the Bar Kochva Revolt.
Words of the Week
Also I have seen under the sun, that in the place of law there is evil, and in the place of justice there is evil.
– King Solomon (Ecclesiastes 3:16)

 Shlomo Gerzovsky (1913-1997) was born in Uman, Ukraine. When the Communist Revolution began, the family fled to Romania, and eventually made its way to the Holy Land. Gerzovsky, now with the Hebraized last name “Gur”, started studying at the Mikveh Israel Agricultural School. In 1936, the Arab Revolt began, with Arab mobs attacking both British nationals and Jewish residents. In response, Gur was among the co-developers of the Homa u’Migdal (“Wall and Tower”) system, a method of building settlements with pre-fabricated protective walls and a watchtower—quickly assembled, sometimes overnight. Gur co-founded the first such settlement, Kibbutz Tel Amal, then helped to establish a whopping 56 others. All settlements were built legally according to existing Ottoman law, on land purchased by the JNF. They served as safe havens for Jews during the violent Arab pogroms, and ensured that Jewish life in the Holy Land would continue to flourish. In 1945, Gur travelled to the US to further his scientific studies. He returned in 1947 to fight alongside the Haganah, and was placed in charge of overseeing weaponry. Soon after, he established and directed Israel’s new Science Corps (heil hamadah), the focus of which was developing new weapons to protect the State of Israel. Together with
Shlomo Gerzovsky (1913-1997) was born in Uman, Ukraine. When the Communist Revolution began, the family fled to Romania, and eventually made its way to the Holy Land. Gerzovsky, now with the Hebraized last name “Gur”, started studying at the Mikveh Israel Agricultural School. In 1936, the Arab Revolt began, with Arab mobs attacking both British nationals and Jewish residents. In response, Gur was among the co-developers of the Homa u’Migdal (“Wall and Tower”) system, a method of building settlements with pre-fabricated protective walls and a watchtower—quickly assembled, sometimes overnight. Gur co-founded the first such settlement, Kibbutz Tel Amal, then helped to establish a whopping 56 others. All settlements were built legally according to existing Ottoman law, on land purchased by the JNF. They served as safe havens for Jews during the violent Arab pogroms, and ensured that Jewish life in the Holy Land would continue to flourish. In 1945, Gur travelled to the US to further his scientific studies. He returned in 1947 to fight alongside the Haganah, and was placed in charge of overseeing weaponry. Soon after, he established and directed Israel’s new Science Corps (heil hamadah), the focus of which was developing new weapons to protect the State of Israel. Together with 
